


Number of electron pairs: 6 Geometry: octahedral Number of electron pairs: 5 Geometry: trigonal bipyramidal Number of electron pairs: 4 Geometry: tetrahedral Number of electron pairs: 3 Geometry: trigonal planar If the number of electron pairs is 2, geometry is linear. Following are some of the common molecular geometries. Then depending on that number, geometry to the molecule can be assigned. The total number of electrons associated with the framework should be divided by 2, to give the number of σ electron pairs. If there is an overall charge to the molecule, it should also be assigned to the central atom. The central atom electrons that are involved in the π bonding should be subtracted.

The coordination geometry is determined by the σ framework only. All single bonded groups are assigned as shared electron pair bond type. Then the number of valence electrons around the central atom should be determined. In order to determine the geometry, first the Lewis structure of the molecule has to be drawn. Double bonds occupy more spaces than a single bond.Lone pairs occupy more space than bonding pairs.The bonding pairs and lone pairs around any atom in a molecule adopt positions where their mutual interactions are minimized.Some atoms in a molecule may also possess pairs of electron not involved in bonding.Atoms in a molecule are bound together by electron pairs.Further, following assumptions are made by the VSEPR method. In this method, it is assumed that the geometry of a molecule depends only upon electron- electron interactions.
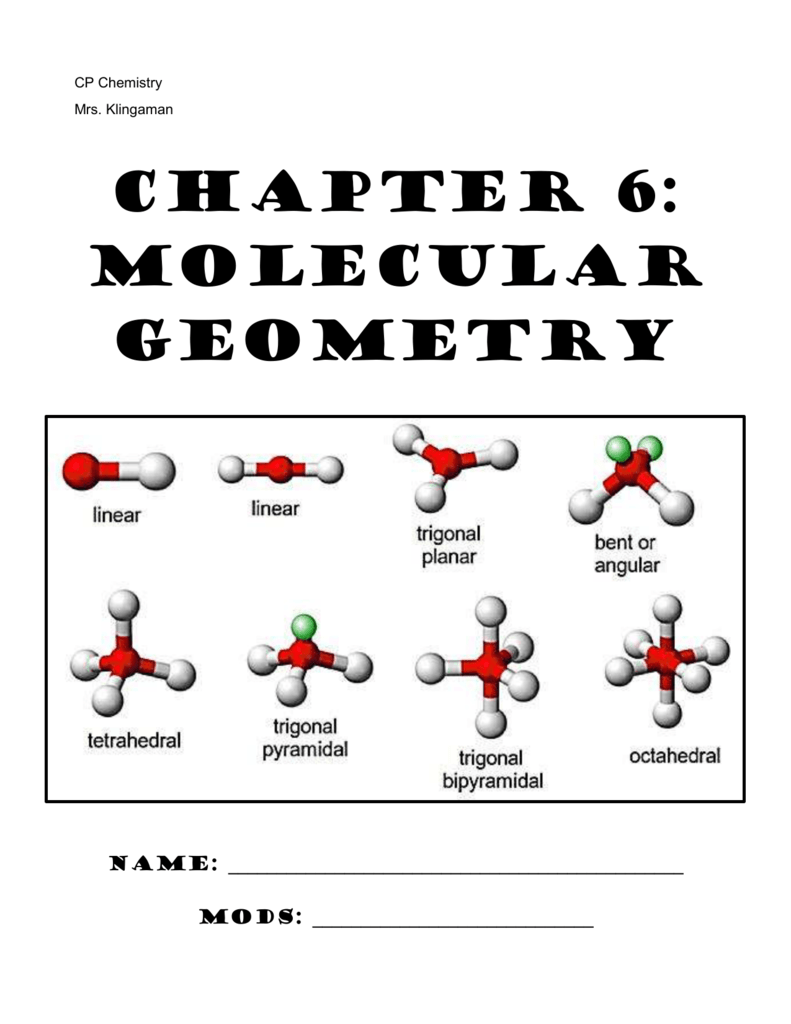
To apply the VSEPR theory, we have to make some assumptions about the nature of bonding. Valence shell electron pair repulsion or VSEPR theory predicts the molecular geometry by this method. In this method, the geometry of a molecule is predicted by the number of valence electrons pairs around the central atom. Experimentally the molecular geometry can be observed using various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. However, if the molecular geometry is determined by the VSEPR method, only the bonds should be taken into consideration, not the lone pairs. VSEPR theory is a model, which can be used to predict the molecular geometry of molecules, using the number of valence electron pairs. Therefore, we can determine the geometry of a molecule by considering some rules. Molecules with the same number of atoms and electron lone pairs tend to accommodate the same geometry. Atoms are arranged in this way, to minimize the bond-bond repulsion, bond-lone pair repulsion and lone pair-lone pair repulsion. Molecular geometry is the three dimensional arrangement of atoms of a molecule in the space. Linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, tetrahedral, octahedral are some of the commonly seen geometries. There are various methods of determining the geometry. The geometry of a molecule is important in determining its properties like color, magnetism, reactivity, polarity, etc. Electron Pair Geometry vs Molecular Geometry


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
